k8s-101 Installation Guide
To participate in the workshop, you’ll need the following tools and accounts.
General tools
Git and GitHub
You’ll need git installed and a GitHub account to complete the workshop.
- Create a new GitHub account here
- Download and install git following these instructions
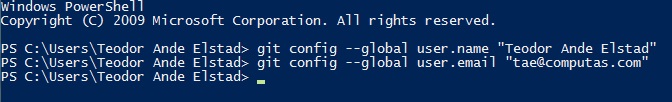
- When git is installed, you should be able to set your username and commit email address. Use the same email that you registered at GitHub.
Azure and C#
All code examples will be given in .NET Core, and we’ll create our Kubernetes cluster on Azure.
.NET Core 3.1 SDK and VS Code
If you already have .NET Core installed, you can check the version with dotnet --version.
- Install the .NET Core 3.1 SDK
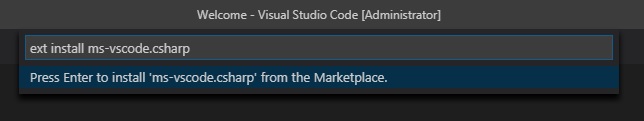
- If you don’t already have a preferred editor for C# code, grab a copy of VS Code. You’ll also want to get the C# extension. Install it by pressing Ctrl+P, pasting
ext install ms-vscode.csharpinto the window and pressing enter.
Azure free trial
If you don’t have an active Azure account with available credits, the easiest option is to grab an Azure free trial account. Just go through the registration process, verify your account, and at the end you should be able to visit the Azure portal. You unfortunately have to register both a phone number and a debit or credit card, but Microsoft won’t charge you if you don’t upgrade the account.
If you already have used the Azure free trial, then you’ll have to register a new account with a new email. You can use the same phone number during the registration process.
Docker and Kubectl
We’ll use Docker as our container technology, and kubectl to manage out Kubernetes cluster.
Docker
- You’ll need Docker in order to containerize applications. Depending on your plattform, the installation can be quite different.
- It you’re running Windows or Mac, we recommend installing Docker Desktop for Windows or Docker Desktop for Mac. If you’re running Linux, we recommend getting Docker CE. If you’re using an older version of Windows, you’ll need to install Docker Toolbox.
- After installing Docker, it’s important that you verify your installation by running
docker run hello-worldin your terminal of choice:
$> docker run hello-world
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.
(amd64)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://hub.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/engine/userguide/
Note: Depending on how you installed Docker on Linux, you might have to run docker commands with sudo.
Kubectl
- Download and install kubectl by following the guide for your platform. Note: It you’re already using Google Clud SDK, you can use
gcloud-command to install kubectl. - Verify your installation by running
kubectl versionin your favorite terminal:
$> kubectl version
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"9", GitVersion:"v1.9.7", GitCommit:"dd5e1a2978fd0b97d9b78e1564398aeea7e7fe92", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2018-04-19T00:05:56Z", GoVersion:"go1.9.3", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"11", GitVersion:"v1.11.9", GitCommit:"16236ce91790d4c75b79f6ce96841db1c843e7d2", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2019-03-25T06:30:48Z", GoVersion:"go1.10.8", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
Note: We won’t be using Minikube, and will instead relying on Azure to set up a new cluster. In other words, just install kubectl, not Minikube.